
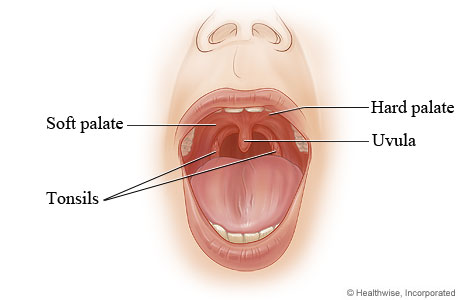

Canker soresĬanker sores are small red, yellow, or white sores that can be painful and cause difficulty swallowing. It can be caused by things like infection, allergies, or trauma. Swollen uvulaĪ swollen uvula, or uvulitis, is generally temporary, but it may make it difficult to swallow or breathe. This condition is generally treated through surgery. Left untreated, food may get into the nose or impact speech.

With a cleft palate, there’s an incomplete separation between the nose and the mouth. Generally, treatments involve surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Oral cancers are typically identified by an ulcer in the mouth that becomes painful over time. Tobacco and alcohol use increase the chance of soft palate and oral cancers. Some conditions that can affect the soft palate include: Soft palate cancer and oral cancers In addition to injuries, the soft palate can experience other conditions such as diseases and problems with its formation. doi:10.1001/archotol.Are there other conditions that can affect the soft palate? Risk factors for serious complication after uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Kezirian EJ, Weaver EM, Yueh B, Khuri SF, Daley J, Henderson WG. Relocation pharyngoplasty for obstructive sleep apnea. Z-palatoplasty (ZPP): a technique for patients without tonsils. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2005.03.061įriedman M, Ibrahim HZ, Vidyasagar R, Pomeranz J, Joseph NJ. Transpalatal advancement pharyngoplasty outcomes compared with uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Surgical correction of anatomic abnormalities in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Lateral pharyngoplasty: a new treatment for obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty: a new technique for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. Obstructive sleep apnea surgery practice patterns in the United States: 2000 to 2006. Kezirian EJ, Maselli J, Vittinghoff E, Goldberg AN, Auerbach AD. Transpalatal advancement pharyngoplasty for obstructive sleep apnea. Relocation pharyngoplasty incorporates very little tissue removal with sewing together the muscles on the side of the throat in a specific way.Z-palatoplasty is associated with more difficulty with swallowing following surgery than other palate procedures. This can be most effective for patients with scarring on the sides of the throat, which can occur after tonsillectomy or previous other soft palate procedures. Z-palatoplasty requires partially dividing the soft palate in the middle and pulling each half forward and laterally.After removal of the bone, the soft palate is then pulled forward and sewn into place. Palatal advancement pharyngoplasty treats the palate by removing some of the bone on the roof of the mouth (hard palate) in the area toward the back, where it meets the soft palate.Effectively, it makes the soft palate shorter without removing muscle, because muscle removal would be expected to affect normal swallowing. The procedure involves almost no removal of the muscle of the soft palate instead, the lining of the mouth (mucosa) over a portion of the soft palate is removed to allow folding of the soft palate muscle. Uvulopalatal flap is used in patients with thin soft palates.
SOFT PALATE TRIAL
This procedure is more involved than UPPP but has also shown better results among a selected group of patients in a randomized trial comparing the two. It involves some tissue removal, but also more extensive repositioning of soft palate tissue (roof of the mouth), as well as the lateral pharyngeal tissues (side of the throat).

In this procedure, the muscle directly behind the tonsil (palatopharyngeus muscle) is freed up from the side of the throat and anchored forward and laterally.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
